Product Overview
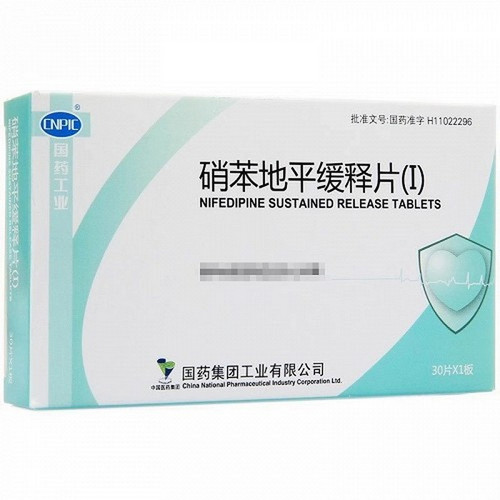
[Drug Name]
Generic Name: Nifedipine Sustained-Release Tablets (I)
Trade Name: Hengxin Nifedipine Sustained-Release Tablets (I) 10mg*48 Tablets
Pinyin Code: HengXinXiaoBenDiPingHuanShiPian (I) 10mg*48 Tablets
[Main Ingredient]
Nifedipine.
[Properties]
This product is a film-coated tablet that appears yellow after the film coating is removed.
[Indications/Main Functions]
1. Hypertension (alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs). 2. Angina pectoris: especially variant angina.
[Specifications]
10mg*48 Tablets
[Dosage and Administration]
1. Swallow the whole tablet on an empty stomach. Do not chew or break it into pieces. 2. Start with a low dose. The initial dose is 20mg/time, and the maximum dose is 60mg/time, once daily. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 120mg. 3. The dose of nifedipine should be adjusted gradually based on patient tolerance and angina control. Blood pressure should be monitored before increasing the dose. If symptoms are significant, the dose adjustment period may be shortened based on the patient's response to the drug. 4. Even if rebound symptoms are not observed upon discontinuation of the drug, the dose should still be gradually reduced, and the patient's condition should be closely monitored. 5. The dose of the standard formulation can be safely substituted for the dose of the extended-release formulation. For example, a 30 mg dose of the standard formulation three times daily can be replaced with a 90 mg dose of the extended-release formulation once daily.
[Adverse Reactions]
1. Liver: Jaundice and elevated glutamate oxaloacetate aminotransferase and glutamate pyruvate aminotransferase levels may occasionally occur. 2. Circulatory System: Chest pain, headache, flushing, dizziness, palpitations, decreased blood pressure, and lower limb edema may occasionally occur. 3. Allergies: Allergic symptoms such as hives and itching may occasionally occur. 4. Digestive System: Abdominal pain, nausea, loss of appetite, and constipation may occasionally occur. 5. Oral: Gingival hypertrophy may occur. 6. Metabolic Abnormalities: Occasional symptoms of hyperglycemia may occur.
[Contraindications]
Contraindicated in patients allergic to nifedipine.
[Drug Interactions]
1. When used in combination with nitrates, this drug controls angina attacks and is well tolerated. 2. When used in combination with beta-blockers, this drug is well tolerated and effective in most patients, but may induce and aggravate hypotension, heart failure, and angina in some patients. 3. When used in combination with digitalis, blood digoxin concentrations may increase. Therefore, digoxin blood concentrations should be monitored during initial use, dose adjustments, or discontinuation of this drug. 4. When used in combination with highly protein-bound drugs, such as dicoumarols, phenytoin, quinidine, quinine, and warfarin, the free concentrations of these drugs often change. 5. When used in combination with cimetidine, peak plasma concentrations of this drug are increased; therefore, dosage adjustments should be made accordingly. 6. When grapefruit juice is taken with this drug, the Cmax and AUC of this drug are increased.
[Precautions]
1. Hypotension: Most patients experience only mild hypotension after taking nifedipine, but some patients experience severe hypotension. This reaction often occurs during dose adjustment or increase, especially when taking β-receptor blockers. Blood pressure should be monitored during this period, especially when taking other antihypertensive drugs. 2. Peripheral Edema: Mild to moderate peripheral edema may occur in patients proportional to the dose and is related to arterial dilation. Edema often initially occurs in the lower extremities and can be treated with diuretics. In patients with congestive heart failure, it is important to determine whether the edema is due to further deterioration of left ventricular function. 3. Diagnostic Interference: Elevations of alkaline phosphatase, creatine phosphokinase, lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, and alanine aminotransferase may occasionally occur with this drug. While generally asymptomatic, cholestasis and jaundice have been reported. Platelet aggregation is decreased, bleeding time is prolonged, and a positive direct Coomb's test with or without hemolytic anemia may be present. 4. Caution should be exercised in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency or those currently taking beta-blockers. A low dose should be initiated to prevent the induction or exacerbation of hypotension, which may increase the incidence of angina, heart failure, or even myocardial infarction. Reversible increases in blood urea nitrogen and creatinine have occasionally occurred in patients with chronic renal failure, but the relationship to nifedipine is unclear.
[Pediatric Use]
Safety and efficacy are not yet established.
[Elderly Use]
This drug has a prolonged half-life, and its Cmax and AUC increase. It is important to start with the lowest dose to minimize the incidence of adverse reactions.
[Overdose]
Insufficient research data are available. Existing literature suggests that increasing the dose may cause excessive peripheral vasodilation, leading to or exacerbating hypotension. Patients with clinically hypotension due to drug overdose should receive prompt cardiovascular support, including cardiopulmonary monitoring, leg elevation, and monitoring of circulating blood volume and urine output. Vasoconstrictors (norepinephrine) can be used to restore vascular tone and blood pressure, unless contraindicated. Patients with impaired liver function experience prolonged drug clearance, and hemodialysis cannot eliminate nifedipine.
[Pharmacology and Toxicology]
This product is a calcium influx blocker or slow-pathway blocker. It blocks calcium ions from entering cells through channels on the myocardial or vascular smooth muscle membranes. This reduces vascular tone and dilates blood vessels throughout the body, including the coronary arteries, thereby lowering blood pressure and increasing coronary blood supply. Furthermore, it inhibits myocardial contraction, reducing myocardial work and oxygen demand, thereby relieving angina pectoris. At therapeutic doses, it has minimal effect on the function of the atrial and atrioventricular nodes.