Product Overview
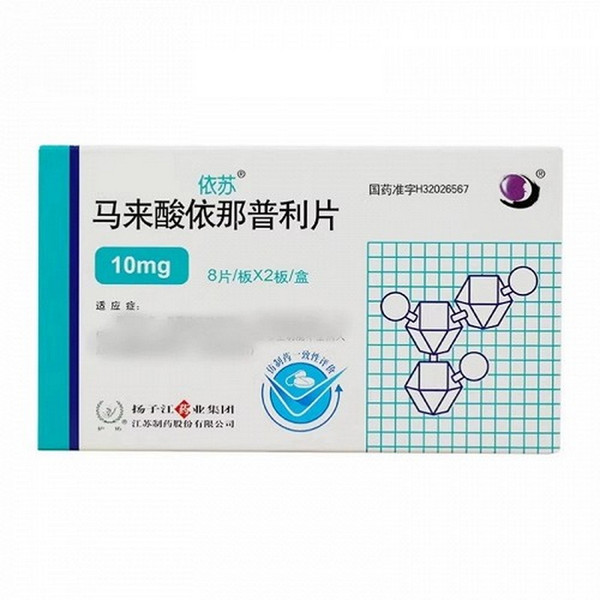
[Drug Name]
Generic Name: Enalapril Maleate Tablets
Trade Name: YiSu
Enalapril Maleate Tablets 10mg x 16 Tablets
Pinyin Code: MalaiSuanYiNaPuLiPian (YiSu)
[Main Ingredients]
The main ingredient of this product is: Enalapril Maleate.
[Appearance]
This product is white or off-white tablets.
[Indications/Main Functions]
Indicated for the treatment of: 1. Essential hypertension of all stages. 2. Renovascular hypertension. 3. Heart failure of all stages. For patients with symptomatic heart failure. Also indicated for: improving survival, slowing the progression of heart failure, and reducing hospitalizations due to heart failure. 4. Preventing symptomatic heart failure. For patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction, it is indicated for: slowing the progression of symptomatic heart failure and reducing hospitalizations due to heart failure. 5. Preventing coronary ischemic events in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Indicated for: Reducing the incidence of myocardial infarction; Reducing hospitalizations due to unstable angina.
[Precautions]
1. Some patients, especially those taking diuretics or experiencing hypovolemia, may experience an excessive drop in blood pressure. Therefore, the initial dose should be started with 2.5 mg. 2. Regularly monitor white blood cell count, renal function, and serum potassium.
[Drug Interactions]
This product is contraindicated in patients with allergies to any component of this product, patients with a history of angioedema from previous treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, or patients with hereditary or spontaneous angioedema.
[Pediatric Use]
Use with caution in children.
[Elderly Use]
As directed by a physician.
[Pregnant and Breastfeeding Use]
Use with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
[Specifications]
10 mg x 16 tablets
[Dosage and Administration]
Can be taken before, during, or after meals. Essential hypertension: Depending on the severity of the hypertension, the initial dose is 10 mg to 20 mg once daily. The usual maintenance dose is 20 mg daily. Renovascular hypertension: Treatment should be initiated with a lower dose (e.g., 5 mg or less). For most patients, a dose of 20 mg once daily achieves the desired effect.
[Adverse Reactions]
May include dizziness, headache, drowsiness, dry mouth, fatigue, upper abdominal discomfort, nausea, chest tightness, cough, rash, flushing, and proteinuria. Reduce the dose as necessary. Discontinue the drug if leukopenia occurs.
[Contraindications]
This product is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to any component of this product, patients with a history of angioedema from previous treatment with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, or patients with hereditary or spontaneous angioedema.
[Overdose]
Not yet established.
[Pharmacology and Toxicology]
This product is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. After oral administration, enalaprilat is hydrolyzed in the body to form enalaprilat, which strongly inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), reducing angiotensin II levels, causing systemic vasodilation and lowering blood pressure. It exhibits significant antihypertensive effects in rat models of renal hypertension (II type II), renal hypertension (I type I), and spontaneous hypertension.
[Pharmacokinetics]
Enalapril is a prodrug. Its ethyl ester moiety is rapidly hydrolyzed in the liver, converting it to its active metabolite, enalaprilat, which exerts its antihypertensive effect. Approximately 68% of enalapril is absorbed after oral administration. Taking this drug with food does not affect its bioavailability. Peak plasma enalapril concentrations reach peak levels 1 hour after dosing. Peak plasma enalaprilat concentrations reach peak levels 3.5 to 4.5 hours after dosing, with a half-life of 11 hours. The conversion of enalapril to enalaprilat is delayed in patients with abnormal liver function. Enalapril is widely distributed throughout the body 20 minutes after administration, with highest concentrations in the liver, kidneys, stomach, and small intestine, and lowest concentrations in the brain. After two days of oral administration, enalaprilat binds to angiotensin-converting enzyme and reaches steady state, with a final half-life of 30 to 35 hours. Enalaprilat is primarily excreted by the kidneys. Patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) may experience drug accumulation; this drug can be cleared by hemodialysis.